Faculty of Science - Research
The scientists of the Faculty of Science are involved in numerous cross-faculty institutions as well as national and international research projects. The scientific performance is visible national and international. Five ERC-grant holders and one winner of the Gottfried Wilhelm Leibniz Prize belong to the faculty. In many externally funded projects (e.g. by DFG, BMBF, EU and some major business enterprises) both basic and application-oriented issues are addressed. The expenditure of funds (excluding expenditure on major equipment) amounts to about 10,1 million euros in 2023 and 10,8 million euros in 2024.
Current cross-sector research associations
Institute for Lightweight Design with Hybrid Systems (ILH)
Lightweight design has a special significance for the conservation of resources in machine, plant and vehicle construction. Against this background the Institute of Lightweight Design with Hybrid Systems (ILH) was set up in September 2012. At present the institute has eleven full members (eight professors of the Faculty of Mechanical Engineering and three professors of the Faculty of Natural Sciences). This allows a holistic view of this lightweight approach and the mapping of the entire process chain of hybrid systems, starting with materials development, based on polymers and metals, continuing with process technologies and simulation techniques and finally ending with aspects of recycling. A special attention is paid to the implementation of consistent lightweight design for increasing the energy and resource efficiency.
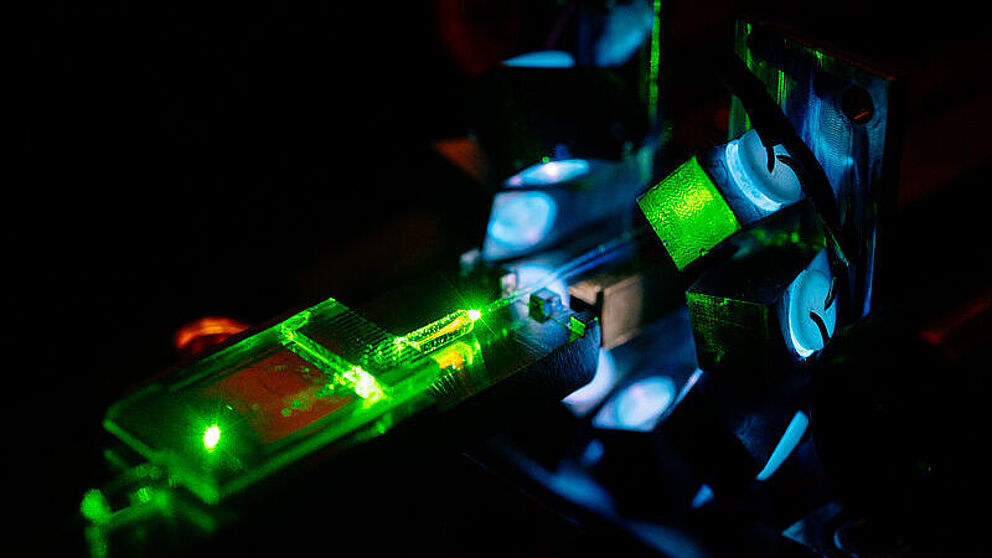
Center for Optoelectronics and Photonics Paderborn (CEOPP)
The CEOPP was established as a central research facility of the University of Paderborn in September 2006. The CeOPP hosts currently 21 research groups from the departments of Physics, Chemistry, and Electrical Engineering. It organizes the use of common technical resources and scientific competences for joint research and development in the field modern optical technologies. This central and common research topic is also an extremely attractive field of education for students in Natural Sciences and Electrical Engineering.
Collaborative Research Center "Tailored nonlinear photonics: From fundamental concepts to functional structures" (SFB/TRR 142)
Under the auspices of the Paderborn Department of Physics research groups of the University of Paderborn (Physics, Electrical Engineering and Information Technology) and the TU Dortmund University (Physics) work together in the SFB/TRR 142. By the combination of Paderborn's expertise in the area of photonic materials, quantum optics, and theory with Dortmund's expertise in the area of nonlinear spectroscopy, an innovative competence center for the study of new information and communication technologies is established. The research program of the SFB/TRR started on 1st of April 2014. For the first funding period of almost four years the program was furnished with a budget of about ten million euros by the German Research Foundation (DFG). On 1 January 2018 the German Research Foundation (DFG) extended the research project with a budget of about 11.5 million euros by four years. After the maximum possible duration of three funding periods, the Collaborative Research Centre/TRR 142 officially ended in December 2025. More Information …
Institute for Photonic Quantum Systems (PhoQS)
The institute founded in 2020 pools the expertise of various Paderborn research groups in developing second generation quantum technologies, which rely on the targeted control and manipulation of single and coupled quantum systems. These novel technologies promise exciting new applications that can outperform their classical counterparts. Quantum communication can be absolutely secure; quantum measurements exhibit precision beyond any classical boundary; and quantum computers will have an enormous computing power. The PhoQS aims in particular on photonic that is, light-based, quantum technologies. This not only strengthens the strategic focus on photonics, opto-electronics, and quantum optics of the Paderborn University, but also bridges the gap to the neighboring fields of mathematics, computer science, and electrical engineering. At the beginning of 2022, construction work began on the new research building "Photonic Quantum Systems Laboratory", or PhoQS Lab for short, which is funded by the Joint Federal Government and State’s Funding Programme.
Center for Sustainable Systems Design (CSSD)
The sustainable use of resources is of central importance to our society. This includes, in particular, a sustainable energy supply from "green" sources such as sunlight or wind. The conversion of surplus energy into transportable energy carriers is equally important. In order to bundle the expertise of our faculty in these areas and to promote synergies and new research approaches, Prof. Matthias Bauer and Prof. Thomas Kühne founded the Center for Sustainable Systems Design (CSSD) in 2019. It comprises research groups from the fields of experiment and application as well as theory and simulation. The development of new systems for the production of hydrogen using sunlight as an energy source is a specific example for the CSSD research. These systems are designed with special attention to sustainability aspects. For example, only base metals that are readily available and biocompatible are used.